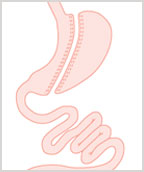
The Procedure:
A surgical stapling device is used to remove the large reservoir section of the stomach. The operation leaves a narrow tubular section of stomach that has 10-15% of the capacity of the original stomach. This narrow tube of stomach carries food to the intestines, without moving intestines or re-routing the flow of food. Patients spend 1-2 nights in the hospital, and recovery time is 1-2 weeks.
The Results:
The stomach fills quickly with small amounts of food, so patients feel satisfied after eating less. Medical research also seems to show that some hunger-related hormones such as ghrelin are reduced or even eliminated by removing the stomach that produces them; the sleeve gastrectomy seems to eliminate some of the hunger system. The sleeve gastrectomy improves health by assisting in significant weight loss and helping to correct the abnormal physiology caused by obesity.
Additional Considerations:
The Sleeve is a relatively new procedure, long-term research won’t be available until around 2020. Some of the risks with sleeve include bleeding, leaks, kinking of the stomach, weight regain, etc. Sleeve is not recommended for patients with significant reflux.